Fact-check: RwandAir isn’t offering government transport subsidies
RwandAir is not giving transport subsidies to citizens. This claim was made to trick unsuspecting internet users and take their sensitive information.
Writer: Nancy Ceasar
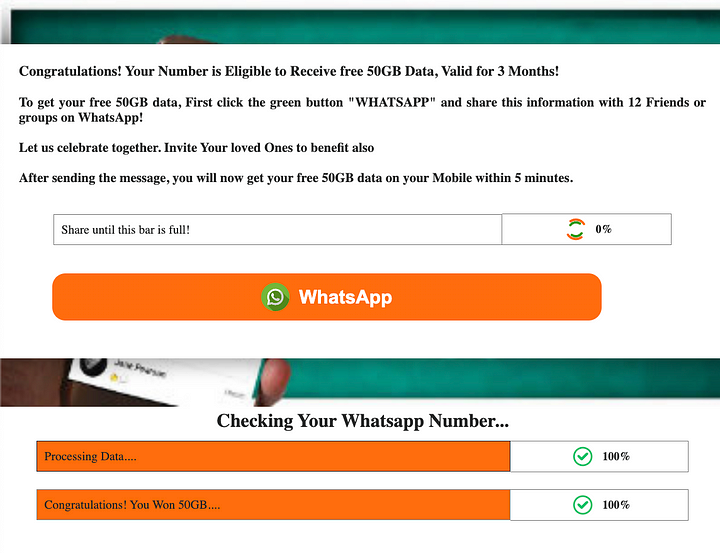
A message was forwarded to many WhatsApp groups and private chats claiming to be Rwanda’s government transport subsidy, giving gifts to their lucky winners with an award of “$1,000,00” after answering some questions.
Then after opening the box, it takes it to another unrelated site, making it suspicious.
The picture on the congratulatory message was used by the Facebook page Rwanda, the heart of Africa, with the caption, “The national carrier, Rwanda, has been named among the most improved airlines in the world. Kigali international airport has also recorded the best-ever passenger traffic #I love Rwanda. Rwanda is a small country with a big dream,” on December 10th 2018.
Investigation:
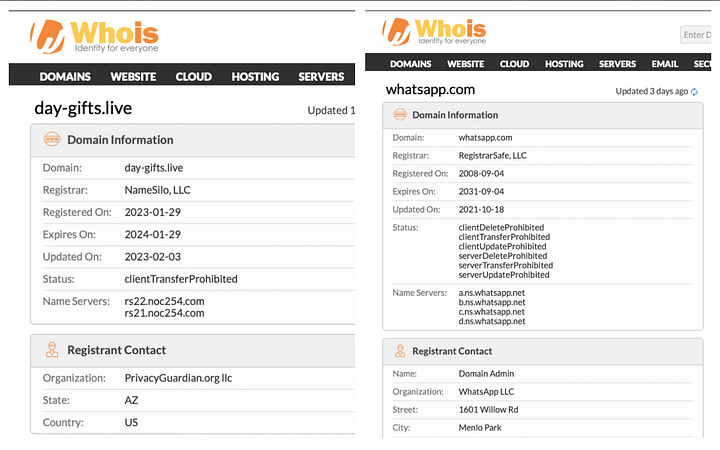
211 Check carried out an examination of the URL using Virustotal, an online tool used to detect malware and other suspicious software. It detected the URL as being a phishing link. Phishing links are links created to promote scams or fraudulent activities, and by clicking on them, one’s information can be stolen and used for selfish reasons or to misuse information for personal gain.
The official website for RwandAir is: https://www.rwandair.com/
In addition, a Google Lens search shows that Pulse used the picture live.co.ke with the caption, “Here is how many passengers the top 10 African airlines managed to airlift in 2018.”
Rwanda Airlines began operating on December 1, 2002, as a new national carrier under the name RwandAir Express [passenger air transportation is the core activity]. Rwanda, with concession, is carrying out airport ground handling ancillary activity at Kigali International Airport.
In March 2009, it was registered with a new trademark, RwandAir, the current operating name. The Rwandan government introduced a 29.3 billion Rwandan franc subsidy to ease the burden on pressed public transport service providers. Information provided by ODA indicates that the government has allocated a subsidy of 29.3 billion Rwandan Francs in the 2021 financial year as a relief payment to hard-pressed public transport operators. Under the now extended covid 19 regulations, Rwandan public transport operators are requested to reduce their load factors to 50% of carrying capacity.
Previously, the same claim had surfaced on the internet and was fact-checked by PesaCheck, as seen in this link.
Conclusion:
211 Check finds that the circular in WhatsApp groups claiming that the government of Rwanda will issue transportation subsidies and every citizen can get them is false. This is a phishing scam where some individuals collect internet users’ details and use them for their interests or sell them to a third party. The general public should be cautious when dealing with information online. Some information is too good to be true, and verification is needed before trusting any link shared on social media.
To ensure accuracy and transparency, we at 211 Check welcome corrections from our readers. If you spot an error in this article, please request a correction using this form. Our team will review your request and make the necessary corrections immediately, if any.
Fighting misinformation and disinformation in the media is crucial to avoiding fake news. Don’t share content you’re uncertain about. False information can harm and mislead people, risking their lives. Fact-check before sharing. For more details, visit https://211check.org/ or message us on WhatsApp at +211 917 298 255. #FactsMatter